By Jesse Peers, Cycling Manager at Reconnect Rochester
I say this on my history bike tours a lot: If I could temporarily time travel back to one decade, it’d be the 1890s. In this decade, the up ‘til then economy-minded City of Rochester started a massive investment in the public realm: it developed its world-class park system and with the electrification and extension of the trolleys, residents could hop on a streetcar and visit our parks and beaches at their leisure. The 1890s is also renowned as the greatest bike boom in history and automobiles hadn’t yet dominated our streets.

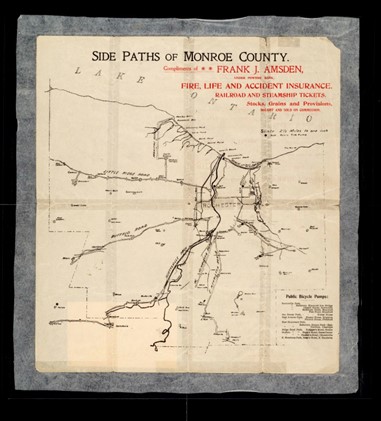
One of the bicycle’s greatest selling points at the time was the ability to access these newly developed parks and to escape the city into nature whenever you wanted. The world was at your fingertips – just a short pedal away! In the early twentieth century, Rochester cyclists would make that access to nature and the surrounding countryside even easier by pioneering a system of sidepaths through Monroe County. For a while, cyclists came to Rochester from afar to see top-notch bike infrastructure!
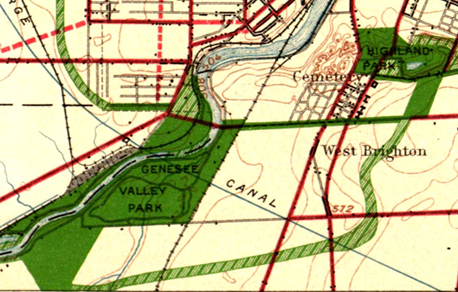
In Rochester’s early days, the city center was surrounded on all sides by “verdant nurseries and blooming orchards.” Visitors to the Flower City were awed by the “seemingly endless acres of blooming rose bushes, tulip beds & fruit trees, encircling the city.” Before those areas were taken over for housing, Rochester’s early Parks Commissioners proposed a park boulevard 300 feet in width encircling the city with a number of small parks scattered along its route. Instead, priority was given to two large parks straddling the river: “South Park” (Genesee Valley Park) and “North Park” (Seneca Park).
That original idea, though, kept resurfacing as subsequent mayors toyed with the idea of connecting the growing park system. Like many, we are mesmerized by this 1911 vision for Rochester. Because Rochester’s large parks were “comparatively remote,” planners felt their usefulness could be “much enhanced by narrow, extending arms reaching out into the surrounding territory and forming park-like approaches to them.” These connective parkways would “multiply in effect the extent of park area conveniently available to the community.”
Sadly, the costs were too prohibitive and the project was dropped. (Two small beginnings though were made towards its realization: Seneca Parkway in Maplewood and Genesee Park Boulevard in the 19th Ward). For an example of a peer city that got much closer to achieving a similar vision, check out Louisville, Kentucky.
With another bike boom happening, the recent adoption of Rochester’s Children’s Outdoor Bill of Rights, the expansion of the City’s Bike Boulevard network, and the simultaneous creation of Active Transportation Plans for the city and county, we thought it a good time to revisit this concept of bike access to nature and our parks. Using the 1911 vision as our guide, let’s examine our modern bike network as connective tissue to our stellar parks.
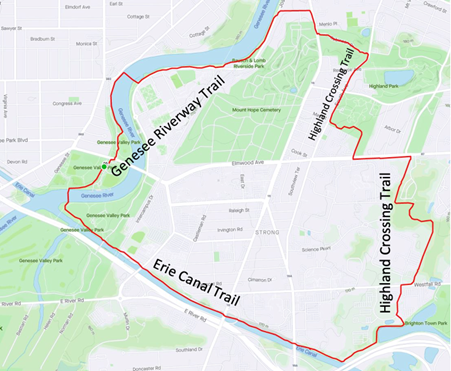
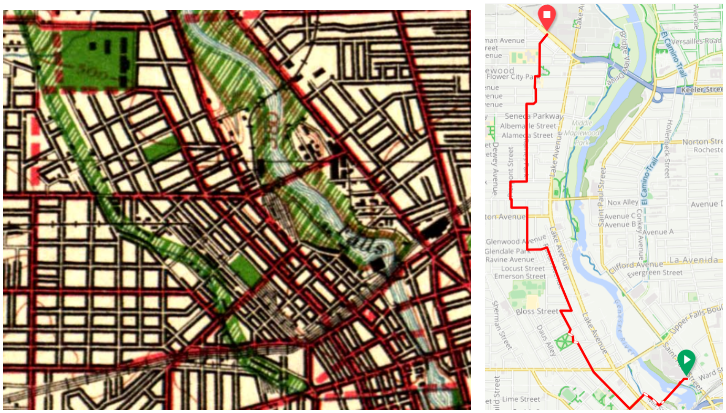
The Highland Crossing Trail, which many residents don’t know about since it hasn’t been incorporated into Google Maps’ bike layer yet, was a unique collaboration between Brighton and Rochester. With the Erie Canal Trail, it connects Genesee Valley Park to Highland Park. These trails together with the Genesee Riverway Trail make a wonderful seven-mile recreational loop we recommend you try sometime.
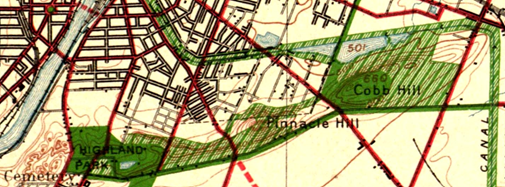
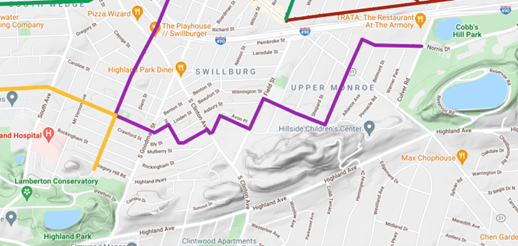
Recurrent calls in the early twentieth century to secure the Pinnacle Hills as parkland connecting Highland Park and Cobbs Hill Park were unsuccessful but today’s Bike Boulevard through Swillburg and Upper Monroe does a good job of connecting them.
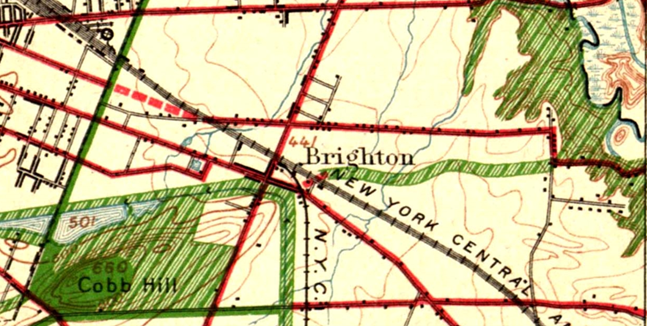
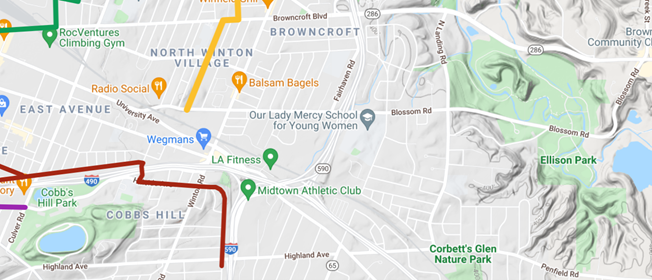
Connecting Cobbs Hill to Irondequoit Bay and what is now Ellison Park is harder. The 1911 planners called for an extension of Richs Dugway Road but today’s railroad tracks present a significant barrier, as does the area around Wegmans and the “Can of Worms” interchange. For now, Browncroft Blvd, Blossom Rd and Highland Ave can be used. Living in the Culver and Merchants triangle, my kids and I are a 10 minute bike ride away from Ellison Park – a ride we cherish, especially in the Fall. We turn off of Browncroft onto Shaftsbury and Corwin Roads for a low-stress approach to the Park.
Though a parkway or trail extending east to west “along the low land just south of the Ridge Road” and today’s 104 isn’t possible, the El Camino Trail and the new Bike Boulevard through 14621 can connect Seneca Park to Irondequoit Bay.
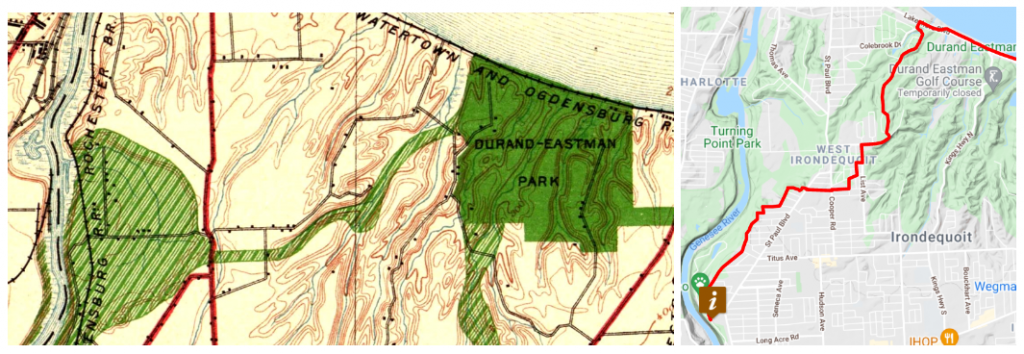
To connect the Genesee River and Seneca Park to Durand Eastman Park, the 1911 plan called for a connection westward “up one of the little valleys” to the northerly end of Seneca Park. Check out this creative route by Pam Rogers.
To connect downtown with Edgerton Park and further north, we all know Lake Avenue must be avoided at all costs by bike. But the new Bike Boulevard along Plymouth parallels Lake Avenue and gets you all the way up to Kodak Park in a low-stress manner through the gorgeous Maplewood neighborhood.
What are your favorite low-stress ways to visit nature by bike? Let us know! If you agree with the Children’s Outdoor Bill of Rights declaration that every Rochester child should be able to “safely explore their community green spaces” and nearby parks, we’d ask you to advocate for continuous, high-comfort bike infrastructure for all ages and abilities for the City and County’s Active Transportation Plans this year.